Artificial intelligence chatbots like ChatGPT, Google Gemini, and Anthropic Claude rely entirely on the prompts we give them. A prompt is simply the instruction or question you type to the AI, and its quality determines how helpful the response will be indianexpress.com. In fact, experts say you don’t need a computer science degree to get good at prompting – it’s a skill anyone can learn with practice indianexpress.comhelp.openai.com. Writing effective AI prompts produces accurate, relevant answers; vague or incomplete prompts lead to confusion. For example, instead of saying “Write a summary,” a clearer prompt is, “Write a summary of this article in 5 bullet points focusing on economic implications for the IT sector.” This kind of detail guides the AI and yields much better output indianexpress.com.
Why Good Prompts Matter
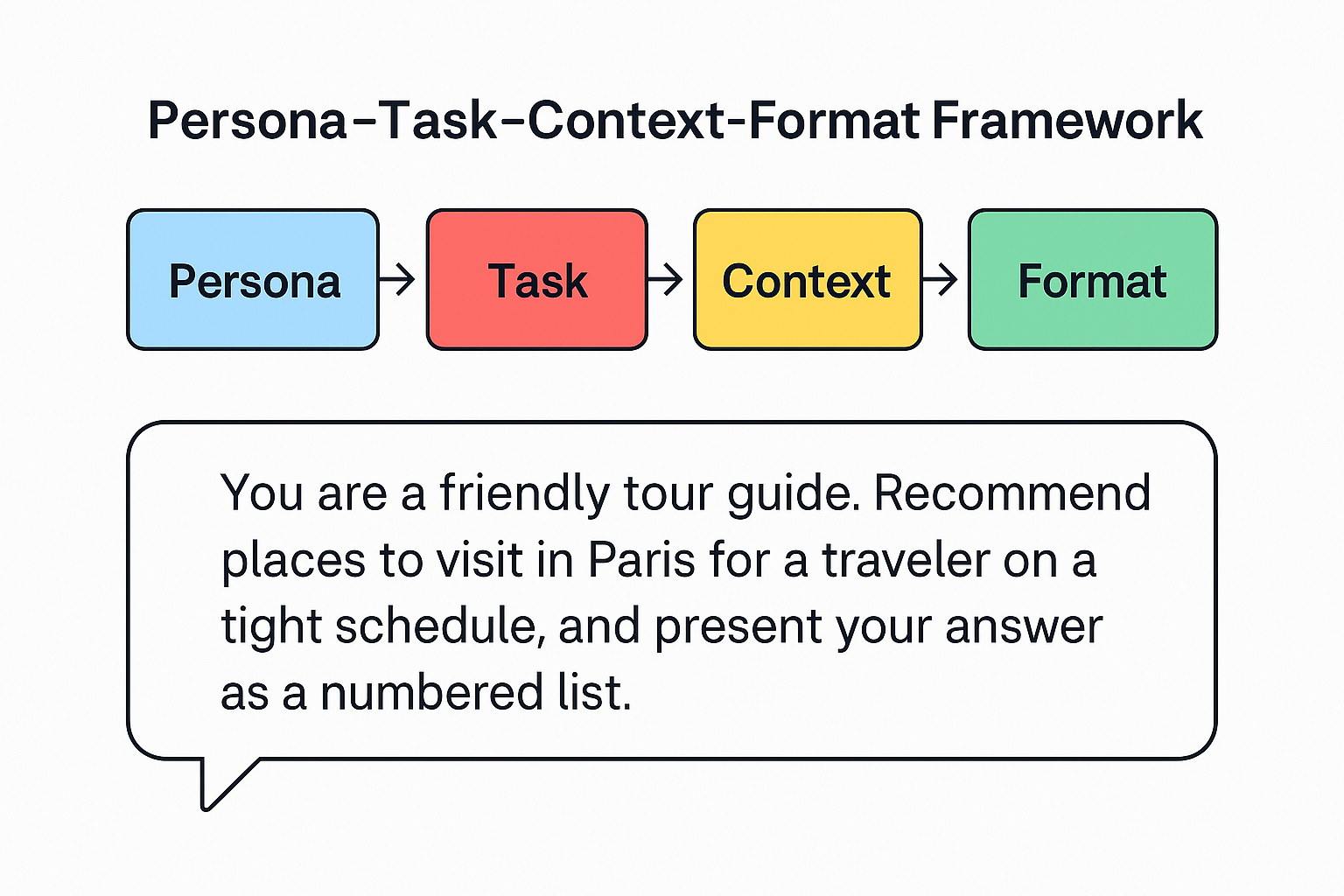
AI models don’t “know” what you want beyond the words you give them. Think of a prompt as the steering wheel of the AI: it directs the output. According to Google’s guidance, the most effective prompts have four key parts: a persona (who the AI should “be”), a task (what to do), context (background information), and a format (how to structure the answer) indianexpress.cominnovareai.com. For instance, you might say, “You are a friendly tour guide (persona). Recommend places to visit in Paris (task) for a traveler on a tight schedule (context), and present your answer as a numbered list (format).” This level of clarity narrows the AI’s focus and leads to more accurate, useful results innovareai.comindianexpress.com.
By contrast, a vague prompt leaves the AI guessing. As one technology journalist notes, “What happens in vagueness stays in vagueness.” A prompt like “Write something about climate change” is too broad. Instead, specify exactly what you need: for example, “Write a 300-word blog post on the health impacts of climate change, targeting a general audience, and include one example of an affected country.” This clear instruction ensures the AI’s answer hits the right tone, scope, and details indianexpress.comscalenut.com.
In short, effective prompting means being clear, concise, and complete. Use direct action verbs (e.g. summarize, translate, compare, explain, code, list), define the audience or purpose, set length or style limits, and include any necessary details indianexpress.comhelp.openai.com. The more relevant information you pack into the prompt (without overloading it), the better the AI can tailor its answer.
Essential Tips for Crafting Prompts
Here are some beginner-friendly, actionable guidelines to write effective AI prompts:
- Be Clear and Specific. Use precise language and full instructions. Instead of “Tell me about photosynthesis,” say “Explain the process of photosynthesis in three simple steps for a middle-school student.” This avoids ambiguity and narrows the AI’s focus help.openai.cominnovareai.com.
- Provide Context. Give background or constraints that the AI should consider. For example, “As a time-crunched traveler, I have 6 hours in Paris. Recommend top attractions and eateries within walking distance.” Adding context like time limits or user perspective steers the AI toward relevant answers indianexpress.cominnovareai.com.
- Assign a Persona or Role. Sometimes telling the AI who it should pretend to be improves output. For instance, “Act as a career coach and help me write a compelling resume summary for an editorial job.” Specifying “You are a career coach” (persona) changes the style and focus of the response indianexpress.comindianexpress.com.
- Format Your Request. Specify the desired format—such as bullet points, a table, code block, or essay. For example: “List 5 key takeaways from this report in bullet form.” When you say “Format the answer as X,” the AI knows how to structure its reply indianexpress.comseerinteractive.com.
- Use Examples (Few-Shot Prompting). Show the AI what you want. Include one or two examples of the desired output. For example, “Here is a tweet combining humor and stats about climate change: [example]. Now write 5 similar tweets.” Giving examples helps the AI mimic the style or structure indianexpress.comseerinteractive.com.
- Ask Step-by-Step (Chain of Thought). For complex tasks, break them down. You can even instruct, “Explain your reasoning step by step.” This chain-of-thought prompting often yields more logical, detailed answers, especially for coding, math, or planning tasks indianexpress.comseerinteractive.com.
- Iterate and Refine. Don’t expect perfection on the first try. Treat the exchange as a dialogue. If the answer is off, tweak your prompt and try againhelp.openai.comindianexpress.com. You might add details, change wording, or ask follow-up questions. For instance, you can tell the AI, “That’s not quite right—let’s focus more on the environmental impact, not just the economic side.” This back-and-forth approach fine-tunes results indianexpress.comhelp.openai.com.
By applying these principles, your prompts become much sharper. As one prompt-engineering guide puts it, “Clarity is king.” Avoid jargon or multi-part questions tangled together. Give the AI clear instructions and any necessary background.
Examples: Good Prompts vs. Bad Prompts
Seeing prompts side-by-side can highlight the difference. Below are some beginner-friendly examples comparing vague prompts with improved versions:
- Topic Clarity (Writing).
- Bad: “Write something about meditation.”
- Good: “Write a paragraph about the benefits of meditation for mental health.”scalenut.com.
The improved prompt specifies what (“the benefits of meditation”) and for whom (“for mental health”), so the AI knows the target.
- Summaries and Length.
- Bad: “Write a summary of the article on artificial intelligence.”
- Good: “Write a 200-word summary of the article on artificial intelligence.”scalenut.com.
By adding a word count or length, the AI knows how much detail to include. Similarly: “Summarize this text in 3 bullet points” or “Create a summary of this article in 2-3 sentences” gives clear formatting instructionsmedium.comindianexpress.com.
- Structure and Details (Blog Post).
- Bad: “Write a blog post about public speaking.”
- Good: “Write a blog post (500 words) about practical tips to improve public speaking skills, aimed at beginners.”scalenut.com.
The good prompt defines length, focus (tips to improve skills), and audience (beginners), leading to a targeted answer.
- Product Descriptions (Keywords).
- Bad: “Write a product description for a laptop.”
- Good: “Write a product description for a laptop with an Intel Core i7 processor and NVIDIA graphics card, highlighting its performance features.”scalenut.com.
Including specific keywords (CPU, GPU) guides the AI to mention the right specs, rather than giving a generic description.
- Recipe Instructions (Specificity).
- Bad: “Write a recipe for pumpkin soup.”
- Good: “Write a recipe for a vegan pumpkin soup with a cashew cream topping.”scalenut.com.
The good prompt specifies vegan and topping, so the AI can include those details.
- Role or Persona (Creative Writing).
- Bad: “Give me travel tips.”
- Good: “You are a travel blogger. Give me 5 budget-friendly travel tips for a week in Spain, in a friendly, first-person tone.”
The improved version assigns a role (“travel blogger”) and tone (“friendly, first-person”), which steers the style of the response.

These examples illustrate that additional detail and clear instructions turn a so-so prompt into a great one. Always ask yourself: What exactly do I want? Who is this for? In what format? Then include that in the prompt.
Tips for Different Use Cases
Different tasks may require different prompt strategies. Here are some tips for common use cases:
- Writing & Content Creation: Specify the format (e.g. article, listicle, email), audience, and tone. For example: “Write a friendly, 150-word blog introduction about the benefits of daily meditation.” If editing content, prompt the AI to critique or improve: “Here is a draft paragraph; improve its clarity and style.” Use examples of voice or style if you have them.
- Coding & Technical Tasks: Clearly state the programming language and the problem. For instance: “Write a Python function that takes a list of numbers and returns the median. Include error handling for empty lists.” When asking for code, it’s helpful to mention best practices: “Generate the code with clear comments explaining each step.” You can also ask the AI to review or explain code. For example, paste a code snippet and say, “Review the following code for bugs and readability, and suggest improvements.” Including requirements like language/framework, desired output, and edge-case handling will yield better results than a generic “Write code to do X.”
- Research & Data Gathering: If you need factual information or analysis, frame the prompt like a research question. You can instruct the AI to show its reasoning. For example: “Explain step by step how photosynthesis works, as if teaching a high school student.” Asking “Explain your reasoning” or “Think step by step” can produce more logical answers indianexpress.com. For complex queries, break them into parts. Also, be aware that AI may hallucinate facts. Wherever possible, double-check answers against trusted sources. When asking for data summaries (like extracting numbers or trends), you can supply the data or context and say “summarize the key insights.” If your AI tool supports it, upload relevant files and prompt, e.g., “Using the attached report, summarize the main findings in bullet points.” This is possible with tools like ChatGPT, Gemini, or Claude that accept file inputs indianexpress.com.
- Summaries: AI can create quick summaries of articles or long text. A simple trick is using “TLDR” in the prompt: e.g., “TLDR: [paste text]” will yield a concise overview medium.com. Better still, specify the length or format: “Summarize the following article in 300 words” or “Write the main points of this text as five bullet points medium.com.” Remember to include the text (or a link if the model can browse) and ask the AI to rely only on the provided content medium.com. Always read the summary carefully: ensure it didn’t add extra info not in the source. AI summarizers are fast, but they can mix in training data if not directed otherwise medium.com. For critical research, use AI summaries as a starting point, then verify and expand them yourself.
By tailoring your prompt to the task – whether you’re drafting an email, writing code, analyzing research, or summarizing an article – you harness the AI more effectively. In all cases, clarity and context remain key: tell the AI exactly what you want in the format you need.
ChatGPT vs. Other AI Tools: Focusing Your Content
Many people immediately think of ChatGPT when it comes to AI chatbots, since it’s been the most famous. However, Google’s Gemini and Anthropic’s Claude are also powerful LLMs with their own strengths. Gemini, for instance, integrates Google search and tends to be tuned for SEO-friendly content, while Claude often emphasizes helpfulness and safety.
For our blog, should we write specifically about ChatGPT or discuss AI tools broadly? The answer depends on your audience and SEO strategy. ChatGPT is widely searched and recognized, so focusing on it can attract readers. At the same time, mentioning Gemini, Claude, and other tools signals that our content is up-to-date and inclusive of the AI landscape. It also captures keywords for those searching other names.
In practice, a balanced approach works best for a small but growing tech site: center the discussion on ChatGPT (as it likely has the highest interest), but also reference Gemini, Claude, and the general idea of “AI prompts.” This way, we optimize for ChatGPT’s popularity without ignoring competitors. For example, we might say “whether you use ChatGPT, Gemini, or Claude, the principles of good prompting are similar,” while still providing any tool-specific tips we know. Over time, watching your analytics will show if readers prefer one focus. But initially, using multiple brand names in your content and headers (like we are doing) can improve search visibility and credibility kyleeggleston.com.
“Using ChatGPT is often versatile, but Gemini’s features may give it an edge in SEO-optimized content” – in other words, each AI has quirks, but good prompting skills apply to all. For our readers curious about AI, this inclusive strategy ensures anyone searching prompt tips for their favorite tool will find our guide.
Conclusion & Next Steps
Effective AI prompting is a skill anyone can learn, and it dramatically improves the value of AI assistants. Remember these key points: be clear and specific, provide context, use examples, and iterate as needed help.openai.comindianexpress.com. Try out the techniques above with your favorite AI (ChatGPT, Gemini, Claude, etc.). Start simple: give a one-sentence instruction and gradually add details to see how the output changes. Experiment with tone, format, and constraints.
Call to Action: Ready to boost your AI productivity? Grab a prompt you’ve used before and refine it using the tips above. For instance, if you asked, “Explain climate change,” try: “Explain the causes of climate change in 5 bullet points, using easy language for middle-schoolers.” See how much sharper the response gets! If you enjoyed this guide, share your success stories in the comments or on social media. Don’t forget to subscribe to gtechtv for more beginner-friendly AI tutorials and tips. Happy prompting!
For More Blogs Visit : GtechtTv